Definition
A learning management system is a software application or web-based technology used to plan, implement, and assess a specific learning process. It is used for e-learning practices and, in its most common form, consists of two elements: a server that performs the base functionality and a user interface (UI) that is operated by instructors, students and administrators.
Typically, an LMS provides an instructor with a way to create and deliver content, monitor student participation, and assess student performance. It might also provide students with interactive features, such as threaded discussions, video conferencing and discussion forums.
Businesses, government agencies, and traditional and online educational institutions often use these systems. They can improve traditional educational methods, while also saving organizations time and money. An effective system lets instructors and administrators efficiently manage elements such as user registration and access, content, calendars, communication, quizzes, certifications, and notifications.
The Advanced Distributed Learning group, sponsored by the U.S. Department of Defence, has created a set of specifications called the Sharable Content Object Reference Model (SCORM) to encourage the standardization of LMSes.
Some popular LMSes used by educational institutions include Moodle, Anthology’s Blackboard Learn and PowerSchool’s Schoology Learning. Popular enterprise-level LMSes include Adobe Learning Manager, Docebo Learn LMS, eFront, iSpring Learn and TalentLMS.
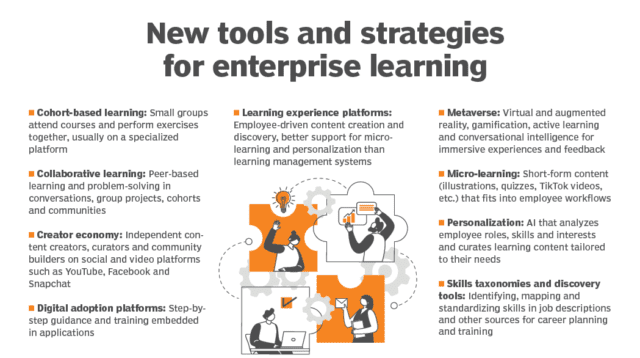
Various new tools are driving online learning options in addition to learning management systems.
What are learning management systems used for?
LMSes are beneficial to a range of organizations, including higher education institutions and companies. They are primarily used for knowledge management: the gathering, organizing, sharing and analysis of an organization’s knowledge in terms of resources, documents, and people skills. The role of the LMS varies according to the organization’s training strategy and goals.
Onboarding and training
Employee training and onboarding are two common uses of LMSes in a business environment. For onboarding, the LMS helps train new employees, providing opportunities to access training programs across various devices. New employees are able to add their own knowledge and provide feedback, helping employers understand how effective the training course materials are and identify areas where new hires need assistance.
An LMS can be used for extended enterprise training purposes as well. This includes customer, partner, and member training. Customer learning activities are common in software and technology companies where user learning goals might include learning how to use a product or system. Ongoing LMS-based customer training improves the customer experience and can increase brand loyalty.
When using an LMS for these purposes, instructors can create immersive learning experiences that let users develop new skills and problem-solving capabilities. For example, an LMS could be used to create tutorials that incorporate augmented reality, virtual reality, and artificial intelligence (AI). This will likely have the effect of improving creativity and innovation throughout the workforce.
Development and retention
Employee development and retention is another way LMSes are used in businesses. The system assigns courses to employees to ensure they are developing effective job skills, remain informed about product changes, and have requisite product and compliance knowledge.
Sales training
Another way LMSes are used is to enhance employee sales skills. This includes the creation of seminars on product knowledge, customer interaction training and case study-based tutorials that use previous experiences with clients to improve future interactions.
Blended learning
An LMS can provide students with blended learning experiences that combine traditional classroom teaching with online learning tools. This method is more effective than simple face-to-face education because it enriches instructor-led training in the classroom with digital learning content customized to fit a student’s learning needs.
How do learning management systems work?
An LMS can be thought of as a large repository where users store and track information in one place. Any user with a login and password can access the system and its online learning resources. If the system is self-hosted, the user must either install the software on their computer or access it via their company’s server.
Some common LMS features include the following capabilities and technologies:
Responsive design:
Users can access the LMS from any type of device, whether it is a desktop, laptop, tablet, or smartphone. The system automatically displays the version best suited for each user’s chosen device and lets users download content for offline work.
User-friendly interface:
The UI lets learners navigate the LMS platform and is aligned with the abilities and goals of the user and the organization. An unintuitive UI risks confusing or distracting users and will make the LMS less effective.
Reports and analytics:
E-learning assessment tools show instructors and administrators how effective online training initiatives are. Both groups of learners and individuals can be analyzed with these tools and metrics.
Catalog and course management:
Admins and instructors manage the catalog of course content in the LMS to create more targeted learning experiences.
Content interoperability and integration:
Content created and stored in an LMS must be packaged in accordance with interoperable standards, including SCORM and xAPI.
Support services:
Different LMS vendors offer varying levels of support. Many provide online discussion boards where users can connect and help each other. Additional support services, such as a dedicated, toll-free phone number, might be available for an extra cost.
Certification and compliance support:
This feature is essential to systems used for online compliance training and certifications. Instructors and admins assess an individual’s skill set and identify any gaps in their performance. This feature also makes it possible to use LMS records during an audit.
Social learning capabilities:
Many LMSes include social media tools in their learning platforms to let users interact with their peers, collaborate, and share learning experiences.
Gamification:
Some LMSes include game mechanics or built-in gamification features that add extra motivation and engagement to courses. This gives students additional incentive to complete courses, in the form of leaderboards, points and badges.
Automation:
Learning management systems automate repeated and tedious tasks, such as grouping, adding, and deactivating users, and handling group enrolments.
Localization:
LMSes often include multilingual support, removing language barriers from learning and training content. Some LMSes integrate geolocation features that automatically present the appropriate version of the course when a user accesses it.
Artificial intelligence:
LMSes use AI to create personalized learning experiences for users with course formats suited to their needs. AI also helps suggest topics a user might find interesting based on the courses they have already completed.
Types of LMS deployments
The different LMS deployment options include the following:
Cloud-based:
LMSes are hosted on the cloud and often follow a software as a service (SaaS) business model. Providers maintain the system and handle updates or upgrades. Online users can access the system apps from anywhere at any time using a username and password.
Self-hosted:
LMSes require the organization to download and install the LMS software. The self-hosted platform provides creative control and customization, but the organization is responsible for maintaining the system and might also have to pay for updates.
Third-party hosted:
LMSes are also learning resources hosted by a third-party organization. Courses can be obtained directly from a public cloud location, or from the training company’s own data center or private cloud.
Desktop application LMSes:
are installed on the user’s desktop. However, the application might still be accessible on multiple devices.
Mobile application LMSes:
support a mobile learning environment and are accessible wherever and whenever through mobile devices. This platform deployment type lets users engage with and track their online learning initiatives on the go.
What are the payment options for LMSes?
The various pricing models used for LMSes include the following:
Freemium:
This free model lets users access the basic features of some LMS platforms for no fee. Once users start engaging with the more advanced functionalities of the system, a fee is imposed.
Subscription:
Users pay a recurring fee at regular intervals to access the LMS. The subscription might grant an organization total access to all LMS features or it might require the organization to pay for each user.
Licensing:
LMS licensing is based on either an annual fee that companies must renew or a one-time fee that provides users with unlimited lifetime access.
Open source:
These products are usually provided at no cost. Some examples are Chamilo, EdApp, Ilias, Moodle and Sakai.
What are the benefits of an LMS?
An LMS can save an organization time and money. Instead of making learners take time out of their day to travel and sit through classes or training at another location, LMSes let them complete the coursework at a time and in a place that is best for them. In addition, LMSes eliminate the need for instructors, training days, training materials, travel expenses and location hiring.
Some other benefits of learning management systems include the following:
- The ability to monitor users’ learning progress and performance.
- Increased e-learning accessibility without geographic limitations.
- Personalized online courses, training and learning experiences.
- The ability to update e-learning modules and activities easily and efficiently.
- Consistent and easy distribution of online training and learning content across an organization.
- Elimination of repetitive tasks, such as user enrollment and certification.
- Centralized learning that lets an organization organize and store all data in one place, making it easier for instructors and admins to update and maintain learning materials.
- Advanced encryption features to keep data and content secure.
Using content management systems with LMSes
An important part of the LMS process is creating the content to be used in the system. If the LMS has its own content, you’ll want to check that it can be changed in response to your organization’s requirements. If you need to create your own content, a content management system (CMS) can be helpful.
A CMS helps produce a variety of content types and includes two components:
- A content management application to design, modify and delete the content.
- A content delivery application that formats the content for its ultimate destination.
Learning experience platforms vs. LMSes
Learning experience platforms (LXPs) are the next generation of learning management technologies. This SaaS-based technology uses AI to adapt the learning experience to the student’s needs and raise the bar on a student’s overall experience. This differs from LMSes, which generally require students to follow a program as the provider designed it.
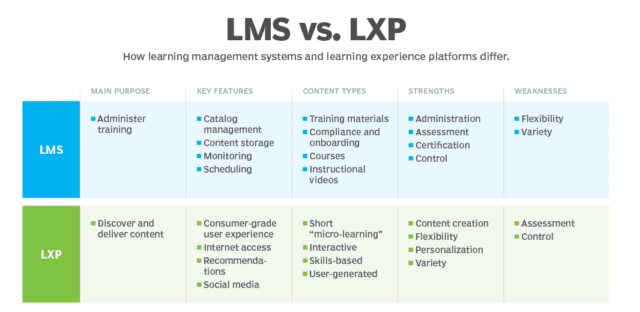
Learning management systems are quite different from learning experience platforms.
The AI component gives students a more autonomous and self-managed experience. For example, if the student indicates an interest in certain information, the LXP presents relevant content from the internet to the student. The LXP also captures data on the student’s preferences and uses it to increase personalization. The goal is to make the training experience more student-centric.
About us:
We are Timus Consulting Services, a fast-growing, premium Governance, Risk, and compliance (GRC) consulting firm, with a specialization in the GRC implementation, customization, and support.
Our team has consolidated experience of more than 15 years working with financial majors across the globe. Our team is comprised of experienced GRC and technology professionals that have an average of 10 years of experience. Our services include:
- GRC implementation, enhancement, customization, Development / Delivery
- GRC Training
- GRC maintenance, and Support
- GRC staff augmentation
Our team:
Our team (consultants in their previous roles) have worked on some of the major OpenPages projects for fortune 500 clients across the globe. Over the past year, we have experienced rapid growth and as of now we have a team of 15+ experienced and fully certified OpenPages consultants, OpenPages QA and OpenPages lead/architects at all experience levels.
Our key strengths:
Our expertise lies in covering the length and breadth of the IBM OpenPages GRC platform. We specialize in:
- Expert business consulting in GRC domain including use cases like Operational Risk Management, Internal Audit Management, Third party risk management, IT Governance amongst others
- OpenPages GRC platform customization and third-party integration
- Building custom business solutions on OpenPages GRC platform
Connect with us:
Feel free to reach out to us for any of your GRC requirements.
Email: Business@timusconsulting.com
Phone: +91 9665833224
WhatsApp: +44 7424222412
Website: www.Timusconsulting.com





